Product Overview
Background
The traditional method for measuring nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity is performed by radiochemical assay that measures the conversion of L-[3H]arginine to L-[3H]citrulline. This method is expensive and requires regulation of radioactive materials. The Ultrasensitive Colorimetric NOS Assay Kit is a low-cost novel assay that allows for the detection of NOS activity without the need for radioactivity. Our Ultrasensitive NOS Assay Kit employs a NADPH recycling system to allow NOS to operate linearly for hours as nitric oxide-derived nitrate and nitrite accumulate. NOS can be assayed spectrophotometrically by measuring the accumulation of its stable degradation products, nitrate and nitrite. The ratio of these two products in biological fluids, tissue culture media, etc. may vary substantially. Hence, for accurate assessment of the total nitric oxide generated, one must monitor both nitrate and nitrite. An excellent solution to this problem is the enzymatic conversion of nitrate to nitrite by the enzyme nitrate reductase (NaR), followed by quantization of nitrite using Griess Reagent. This kit allows for efficient high-throughout screening of NOS activity in resting cells or cell lysates as well as biological fluids and tissue homogenates. The kit is also ideal for in vitro NOS assays using recombinant purified NOS. All materials necessary to perform the entire assay in a 96-well microplate format are provided with the kit.
Assay Principle
NADPH and L-arginine are required for the continual operation of NOS and production of nitric oxide (NO). In aqueous solution, NO rapidly degrades to nitrate and nitrite. Spectrophotometric quantization of nitrite using Griess Reagent is straightforward, but does not measure nitrate. This nitric oxide synthase assay kit employs recombinant nitrate reductase (NaR) for conversion of nitrate to nitrite prior to quantization of nitrite using Griess Reagent — thus providing for accurate determination of total NOS activity.
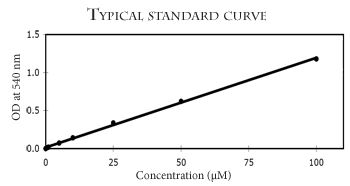
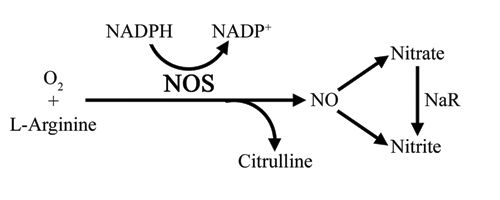 This kit can be used to accurately measure as little as 1 pmol/µL (~1µM) NO produced in aqueous solutions. Very little sample is required (5 to 100 µL depending on the [NO] in the sample). The completed reaction is read at 540 nm.
This kit can be used to accurately measure as little as 1 pmol/µL (~1µM) NO produced in aqueous solutions. Very little sample is required (5 to 100 µL depending on the [NO] in the sample). The completed reaction is read at 540 nm.
References
-
- Ghigo, D., et al. (2006). Nitric Oxide 15:148-153
- Schmidt, H.H., et al. (1995). Biochemica 2:22-23
